Age-related changes in photoaging: correction options
Mesotherapy correction
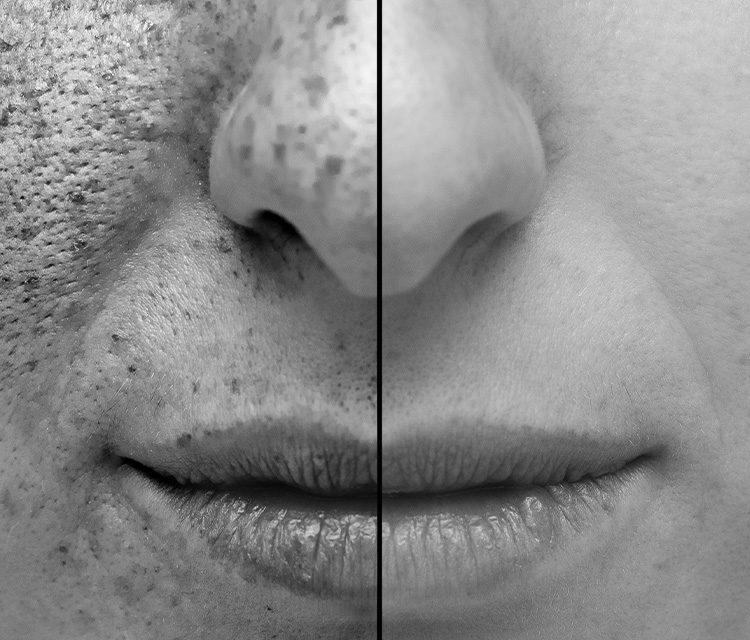
Knowing the pathogenesis and clinical manifestations of photoaging of the skin, let's ask the question: what can we do, firstly, to prevent the appearance and development of signs of photoaging, and secondly, to reduce these manifestations?
Most clinical manifestations of photoaging are due to dermal changes, but changes in the epidermis also occur. Hyperkeratosis can be detected in the stratum corneum of the epidermis. Thickening of the basement membrane, which is observed in most cases, indicates possible damage to keratinocytes. In this case, an uneven distribution of melanocytes of different sizes, pigment accumulation and number of processes is noted along the basement membrane.
Premature skin aging begins with connective tissue, where collagen and elastin fibers are located. Collagen provides skin elasticity, and at a young age its fibers are constantly renewed. The collagenase enzyme destroys old fibers, and new fibers are synthesized in fibroblasts. Under the influence of UV radiation, collagen synthesis in fibroblasts decreases and collagen fibers cross-link. Collagen dimers are inaccessible to collagenase, so they gradually accumulate in the skin. Cross-linking of collagen fibers occurs after each attack of free radicals and leads to a decrease in skin elasticity and the formation of wrinkles.
Full version of the access article in Ukrainian
Read also
- Hyaluronic acid and vitamin B5: the optimal combination for rejuvenation and restoration of sensitive skin
- Injection correction of skin aging: the benefits of bioreparants
- Photoaging: the effects of ultraviolet light on the skin
- Anti-age care programs: how to achieve effectiveness
- Detoxification: process mechanisms and effects on the skin
- Aging and Detoxification: Effects of Toxic Substances on the Skin
- Age-related deformations of facial tissues: how to analyze aging?
- Therapy of skin pigmentation disorders: tranexamic acid and cysteamine
- Rehabilitation of the skin after insolation and prevention of photoaging