Diffuse telogen effluvium hair loss
We have already started talking about diffuse baldness in women and the main aspects of long-term therapy - we looked at androgenetic alopecia and possible methods of its treatment. We continue this painful topic for the fair sex.

Yana Goncharenko , dermatocosmetologist, member of the UADV, trainer in injection techniques and chemical peels, general practitioner, Master of Medicine
Diffuse telogen effluvium is the loss of 100 or more hairs in the telogen phase per day. Depending on the duration, there are acute, lasting up to 6 months, and chronic, over six months, forms of diffuse hair loss. There is an opinion that chronic diffuse baldness is characteristic primarily of females.
The term telogenum effluvium (TE) was first introduced by Kligman in 1961 as a definition of a response to adverse physical and psychological factors that can develop at any age.
Depending on the ratio of anagen and telogen duration, in 1993 Headington JT proposed the following classification.
1. Abrupt cessation of anagen with transition to telogen - hair loss begins 2-3 months after exposure to the initiating factor, which can be:
- psychological stress;
- serious illness or injury;
- taking certain medications.
This type of diffuse hair loss is acute in nature and, after the end of the “initiator” action, is characterized by spontaneous normalization of the hair growth cycle. Acute diffuse alopecia does not require specific treatment.
2. Extension of the anagen phase and synchronization of the onset of telogen - hair loss begins 3-4 months after the end of exposure to the anagen retaining factor and partially stabilizes after 6-8 months. Causes:
- pregnancy and childbirth;
- reception and withdrawal syndrome of contraceptives, especially those with antiandrogenic effects.
Both models have a similar mechanism of falsely “improving” hair quality, and then a fairly rapid loss of density without thinning the hair shafts. It is extremely rare for a patient without trichological help to be able to restore the original picture, since in the vast majority of cases latent, or less often obvious, iron deficiency occurs, especially if borderline levels of iron metabolism already occurred before childbirth or the start of taking contraceptives.
3. Abrupt anagen cessation is an iatrogenic type of hair loss associated with telogen shortening and premature entry into anagen, which is reversible with treatment with minoxidil and minoxidil-like compounds.
4. Short anagen syndrome is chronic diffuse hair loss caused by deficiency conditions and hormonal disorders:
- condition of hair loss of unknown etiology;
- persistent telogen hair loss;
- most clinical situations with periodic hair loss, which does not grow to the desired length.
It is often aggravated by a combination with androgenetic alopecia in females.
5. Telogen elongation and slower transition to anagen - hair loss associated with calendar synchronization - seasonal hair loss. If synchronization of the hair growth cycle in humans is characteristic only in childhood, then seasonal loss, as its residual effects, persists in adults. In our latitudes, the main two peaks occur in February and August.
Diagnostics
The diagnosis of diffuse hair loss is usually straightforward and is based on the 3 “E” principle:
- survey;
- inspection;
- examination.
When interviewing (collecting an anamnesis), it is necessary to find out what events the patient himself associates with the initiation of hair loss, whether the hair loss continues or has ended, what measures were taken and whether they were effective.
During the examination, the somatic status of the patient as a whole is assessed, the presence of inflammatory changes in the skin of the scalp, the prevalence of hair thinning and its patterns, and trichoscopy is performed.
The examination consists of two components: a blood picture and a hair examination.
In the referral for a laboratory blood test, you should indicate the main possible deficient indicators:
- serum iron;
- total iron-binding capacity of blood serum;
- ferritin;
- transferrin;
- zinc;
- copper;
- hydroxyvitamin D;
- folic acid;
- selenium;
- vitamins B6 and B12.
The main hormonal trichological profile is also recommended for monitoring:
- TSH;
- prolactin;
- total and bound testosterone;
- DHEA-s.
A basic hair examination consists of trichoscopy and a tension test, which help to establish the fact of terminal rather than vellus hair loss, to see the preservation of the normal structure of the follicular units and to determine the severity of androgenetic alopecia, if present.
Main causes of chronic TE
The most common triggers for diffuse hair loss in women are:
- psychological stress;
- general anesthesia;
- illness with febrility;
- latent iron deficiency.
Iron
Latent iron deficiency in most cases plays a leading role in the development of TE in women of reproductive age, especially in vegetarians with menorrhagia. And if the role of obvious iron deficiency in laboratory-confirmed anemia is obvious, then regarding latent iron deficiency the opinions of trichologists are divided. It should also be taken into account that the reference values for adults in Ukraine do not correspond to reality. The recommended lower limit of normal for ferritin should be at least 40 ng/ml. It should also be remembered that ferritin is an acute-phase protein and gives falsely elevated results in inflammatory and febrile conditions. In such cases, all indicators of iron metabolism should be assessed, taking into account transferrin saturation. A ferritin level of less than 15 ng/ml indicates a lack of iron stores in the body.
Correcting iron deficiency is a rather lengthy and troublesome process. This is due to the fact that successful therapy is often hindered by poor tolerance to ferrous iron, heavy menstruation, the patient’s lack of discipline in taking medications, and poor absorption in the small intestine with malabsorption syndrome. Starting to take Fe is often accompanied by nausea, stool disorders, bloating, heartburn and even vomiting. The patient should be informed about these unpleasant moments and be ready to choose a comfortable remedy for himself. If undesirable symptoms from the gastrointestinal tract are not relieved, or the patient has concomitant inflammatory diseases of the gastric mucosa, it should be recommended to take ferric iron, which is well tolerated, but only 10% is absorbed.
The target ferritin values to consider the course of treatment complete are at least 70 ng/ml. In the absence of positive dynamics of iron accumulation in combination with menorrhagia, the use of oral contraceptives is recommended to control the volume of monthly blood loss.
Interferon
It is a well-known fact that alpha and gamma interferons used as medicines, for example, for the treatment of hepatitis, are not least among the undesirable effects of hair loss.
This phenomenon is due to the fact that interferons deprive the cells of the hair papilla of the ability to support anagen hair growth. But since health (life) is at stake, payment for this is appropriate. According to the literature, the use of shampoos with zinc pyrithione can reduce such hair loss.
It’s another matter when interferons or, more often, inducers of interferonogenesis are prescribed against the principles of evidence-based medicine by doctors of various specialties and by patients for self-medication. One of the most popular drugs of this kind, often flashed on TV screens, is Amiksin, the active substance is tilorone. By the way, abroad, back in the 80s, clinical studies of this substance were completed ahead of schedule at the preclinical stage due to the development of toxic retinopathy and liver lipidosis. Moreover, tilorone interferes with the pharmacokinetics of P-450 dependent drugs, which is not indicated in the instructions.
However, this drug is widely used for the treatment and prevention of various viral diseases in adults and children, as well as the no less well-known immunomodulator Cycloferon, and identifying the fact of taking such drugs when interviewing patients can often shed light on the true cause of diffuse hair loss.
Another “entertainment” for doctors and patients that leads to TE is the expulsion (often prophylactically) of all kinds of helminths with the use of albendazole or levamisole - substances with pronounced immunomodulatory properties. This kind of prescription is fraught not just with baldness, but with the activation of a wide variety of autoimmune processes that were previously dormant in the body.
Hypothyroidism and hyperthyroidism
Hair loss due to diseases of the thyroid gland (TG) is common, but not always. Therefore, thyroid alopecia cannot be considered an absolute sign of the pathology of this organ.
Hair loss can occur both with an increase and a decrease in thyroid function, and manifests itself both diffusely and in the form of focal lesions. A common accompanying symptom is the loss of eyebrow tails - the so-called Hertog sign. It should be remembered that one of the reasons for hair loss may be the drug itself for correcting thyroid hyperfunction, for example, Mercazolil or Tyrosol, especially if high doses are prescribed for a long time.
For primary screening of thyroid function, TSH is sufficient. It is not advisable to order a study of the entire thyroid panel.
Treatment
Treatment of TE includes all points of therapy for androgenetic alopecia, with the exception of 5-alpha reductase inhibitors:
- identification and cessation of exposure to the etiological factor, if possible;
- topical 2% or 5% minoxidil, or minoxidil-like compounds;
- capsaicin, preferably in combination with nicotinamide and salicylate;
- plasma therapy;
- LLLT (low level laser therapy);
- trichomesotherapy;
- correction of psychological status;
- treatment of iron deficiency;
- use of special trichological peels;
- fractionated non-ablative laser therapy.
Timely treatment can not only stop the progression of chronic alopecia, but also significantly improve the appearance and quality of hair. And since thinning hair in a woman is one of the most common triggers of depression, by taking control of hair loss, we can overcome this personality-destroying condition.
I would also like to note that in the modern world the concept of “preventive trichology” has already been finally formed - both as a separate direction and as part of anti-age medicine in general. The main task of preventive trichology is the prevention and control of diffuse, androgenic and senile alopecia as manifestations of age-related changes in the human pilosebaceous complex.
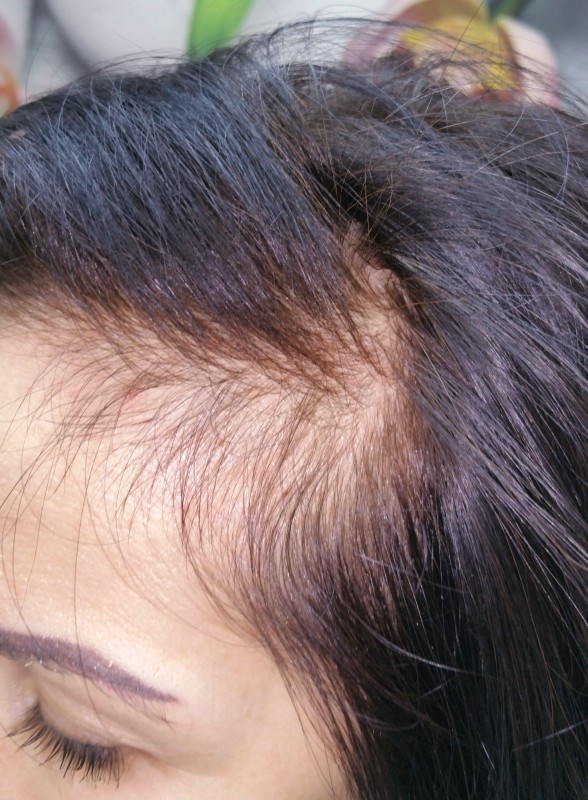
Before
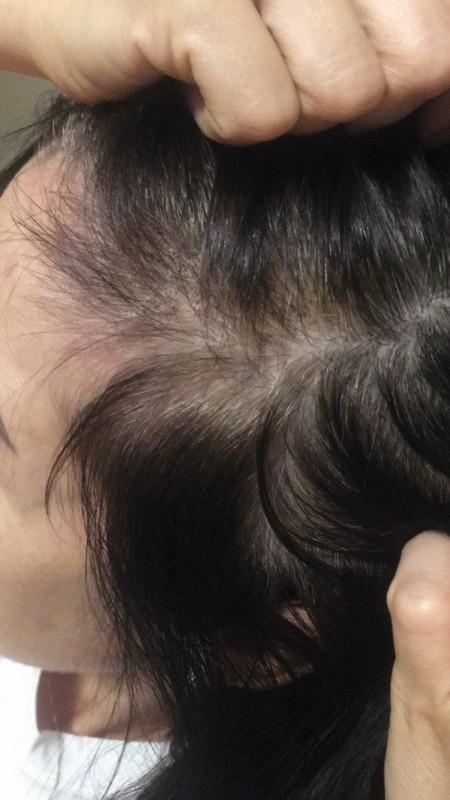
After
In the photo: Before and after treatment for diffuse telogen effluvium
Read also:
Androgenetic alopecia: main aspects of therapy
First published: Cosmetologist No. 1, 2019
