Ultrasonic cavitation: features of the procedure
Standard procedure protocol
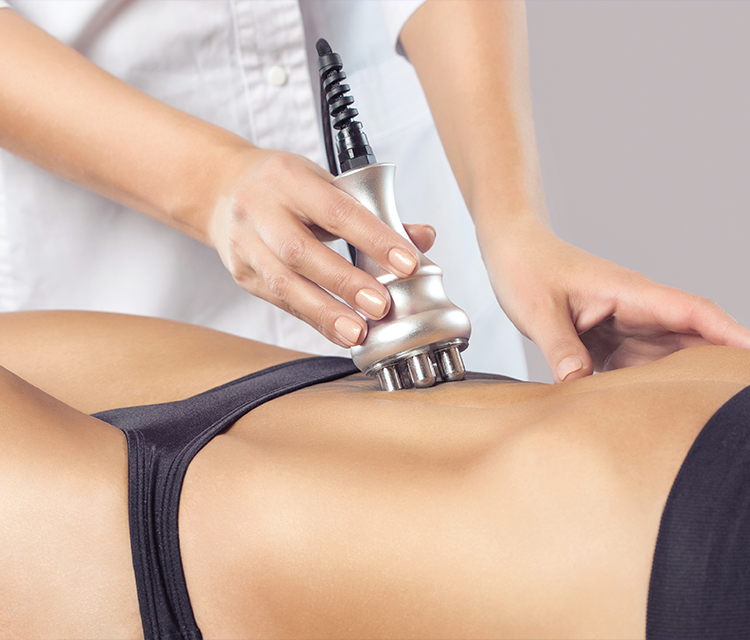
One of the most popular salon procedures for body shaping is ultrasonic cavitation. It is also called non-surgical liposuction, because in the process of cavitation excess fat deposits are removed by a non-invasive method - without surgical intervention.
Yulia Kopetska, dermatologist, cosmetologist, trainer of the "Academy of Scientific Beauty" from the Academie Scientifique de Beaute, Perron Rigot (Ukraine)
Cavitation (from the Latin cavitas - "void") is the process of formation of vacuum bubbles in a liquid medium. In this case, in adipose tissue, because it contains a large amount of liquid.
What happens to the fat during the procedure?
About 75% of the volume of fat cells is a substance we call fat, or triglycerides. During the cavitation procedure, a focused ultrasound wave affects a certain area of the fat layer, where it causes mechanical destruction of fat cell membranes and loosening of fibrous tissue, without affecting blood vessels, peripheral nerve endings and without damaging the skin.
Ultrasonic cavitation destroys fat cells by damaging their membranes and releasing triglycerides, or fats, from these cells. Triglycerides are essentially neutral fats and consist of three fatty acids attached to a glycerol chain. When the adipocyte membrane is destroyed, water-insoluble triglycerides enter the interstitial fluid between the cells, and then, mainly via the lymphatic system, they enter the liver, where they are metabolized, and the breakdown products are excreted naturally.
The phenomenon of ultrasonic cavitation: mechanisms of influence
The cavitation effect causes ultrasound with a frequency of a fairly wide range - from 25 to 50 kHz. However, low-frequency ultrasound (25-32 kHz) affects fatty tissue less effectively. At the same time, large cavitation bubbles appear, which do not have time to collapse and effectively affect fat cells and their compounds. If the frequency of ultrasound is too high (more than 41 kHz), it will lead to the formation of small bubbles that will not be able to exert an intense effect - create a so-called hydrodynamic explosion in the tissues. The most optimal effect is an ultrasonic wave of 40 kHz, but obtaining such a frequency is technically very difficult.
Read also