Fordyce granules
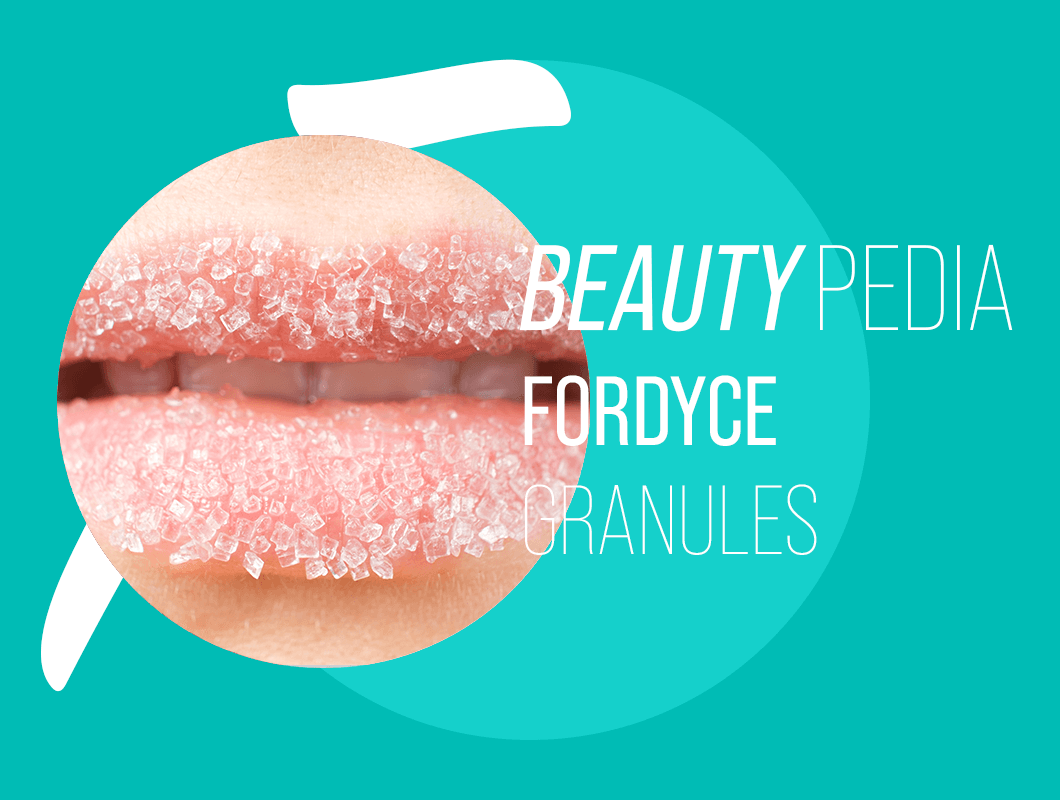
The oral mucosa of a person is often regarded as one that reflects the general state of his health. Fordyce granule lesions are considered a classic and common occurrence. They may be present at birth or appear later in life.
The sebaceous glands are a normal component of the structural elements of the skin. They are also found in the human oral cavity, they are called Fordyce granules, or heterotopic / ectopic. They were first discovered in 1861 by the Swiss anatomist, zoologist and histologist Albert von Kölliker, but named after the American dermatologist John Addison Fordyce, who reported the phenomenon in 1896. Fordyce believed that the presence of such granules could be a sign of an unknown and dangerous disease. But today, most doctors have recognized them as a normal manifestation, formed by the accumulation of sebaceous glands, covered with an intact mucous membrane.
These formations are considered one of the variants of the physiological norm, since they are: completely benign, not harmful to health, not accompanied by unpleasant symptoms, not transmitted during sexual contact or in any other way.
Characteristic signs of Fordyce granules: outwardly, sebaceous gland cysts resemble small, millet-sized nodules (or papules). As a rule, such rashes are numerous, widespread and are not accompanied by pain (neither at rest, nor when pressed on them). When pressing on the formation, in some cases, a very small amount of liquid can be released from it, which has a white-yellow hue and a rather thick consistency. However, more often than not, attempts to squeeze out the contents of the Fordyce granules end in punctate bleeding and the development of hematomas on the skin area surrounding the damaged papule.
